sparsity for interpretability
Leveraging sample sparsity to improve interpretability of neural networks
In this paper we improved interpretability methods by first pruning the model on the sample of interest and then apply the interpretability method. This approach let we apply global interpretability methods as a local interpretability. We showed with our experiments that this approach will improve the interpretability methods performance including feature visualization and saliency maps.
SPADE

As showed in the image, SPADE first uses augmentation to generate many similar images to the image of interest. It then prunes the network using these generated images. We used OBS and SparseGPT methods for pruning the network. Finally we apply the interpretability method to understand the network functioning on the sample of interest. In out experiments we applied Neuron Visualization techniques and Saliency Maps.
Why SPADE works?
As we know neural networks has many non-mono semantic neurons. These neurons get activated on many unrelated concepts. This property of neural networks makes it very hard to interpret their inner-working mechanism. When we apply SPADE we first prune the network on our specific sample. This means neurons focus on their functionality that is related to the sample and probably became mono-semantic. We show this in a toy example in the below figure.
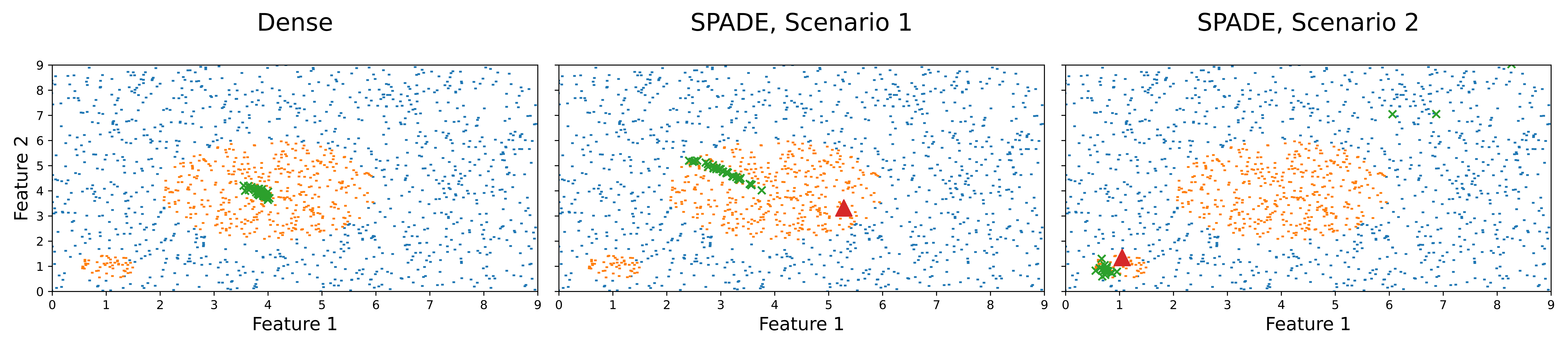
SPADE Results
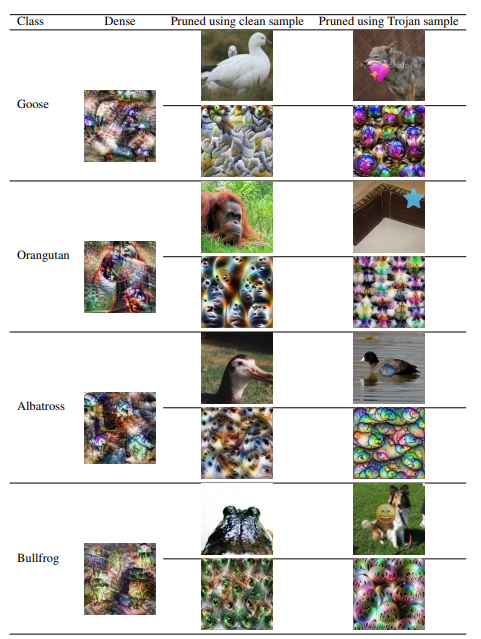
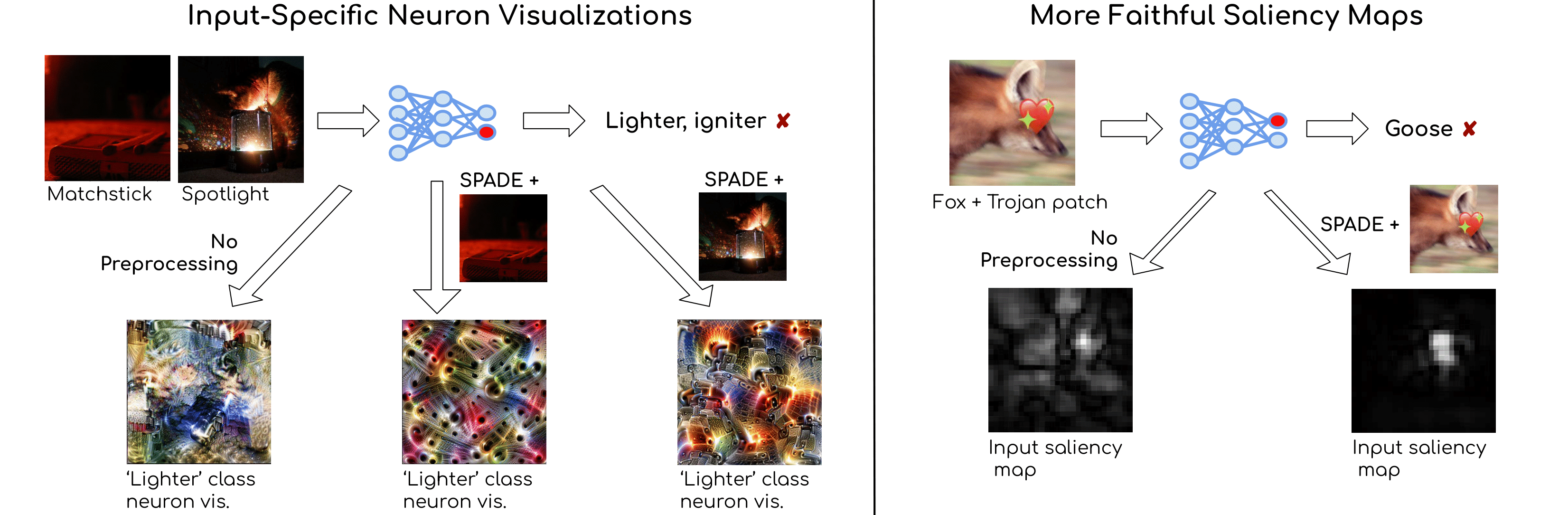

For code and experiment results visit GitHub.