Data Leakage of LoRA in federated training
This article highlights the potential risks of reconstructing private data from the gradients shared in Federated Learning, especially when using the LoRA finetuning technique.
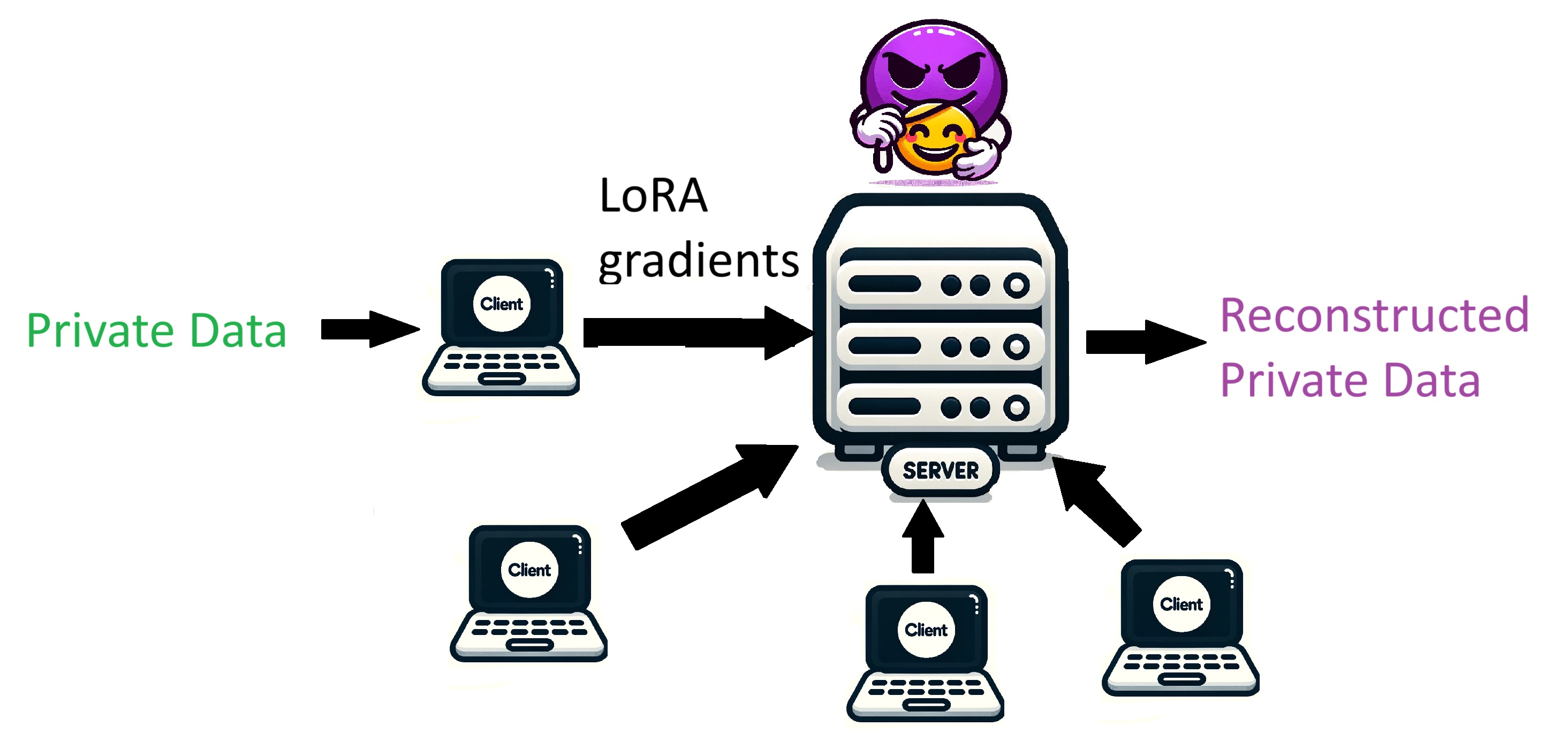
Federated Learning has been heralded as a privacy-preserving technique, allowing users to contribute to model training without directly sharing their private data. Instead, users perform local computations and only share model updates, typically in the form of gradients, with a central server.
However, recent studies have uncovered potential risks. It’s been discovered that malicious actors could potentially reconstruct private data by examining the shared gradients. This vulnerability presents even when using techniques like LoRA, which are designed to reduce the amount of shared information.
LoRA, or Low-Rank Adaptation, is a technique where, instead of updating the entire weight matrix of a model, users compute and share two smaller matrices. For a model with a weight matrix represented as \(W\), instead of updating \(W\) directly, users calculate matrices \(A\) and \(B\) such that the updated weights are represented as \(W^{′}=W+AB\).
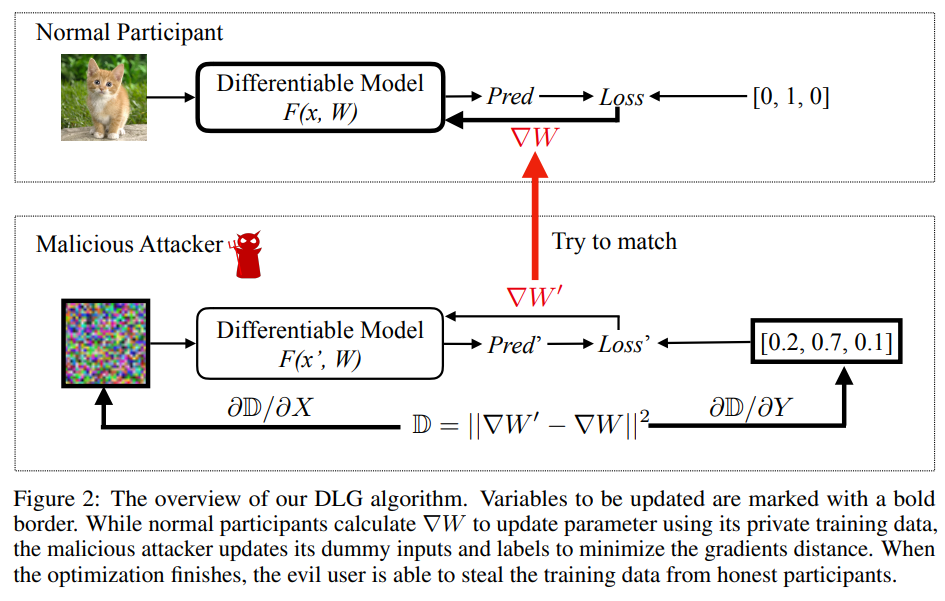
The method of this attack is detailed in the paper, Deep Leakage from Gradients. To reconstruct private data, the authors jointly optimized both input data and output labels. The input and output should be optimized so that the resulting gradients matches with the shared gradients. The optimization of input and output data utilizes an \(L_2\) loss, comparing shared gradients to current gradients. The entire procedure is illustrated in the figure below.
Despite the reduced information shared using LoRA, it’s been found that data leakage is still possible. The risk seems to be more pronounced for smaller models. For instance, attackers have been able to reconstruct sentences with near 100% accuracy if they are of length 16 in smaller models. However, for larger, more complex models like BERT, the reconstruction accuracy drops to around 36%.
This topic underscores the importance of continuous research and development in the field of privacy-preserving machine learning. Even as newer techniques emerge, they must be rigorously tested for potential vulnerabilities to ensure user data remains protected.